IP 分片
IP Fragmentation
IP 分片
IP协议允许Datagram进行分片(英语:fragmentation,又译分段),将Datagram分割成更小的单位。
这样的话,当数据包比链路最大传输单元(MTU)大时,就可以被分解为很多的足够小片段,以便能
够在其上进行传输。
IP 分片引起的问题
- 路由器需要处理分片.reassembly is very inefficient on a router whose primary job
is to forward packets as quickly as possible. A router is not designed to hold on to
packets for any length of time. Also a router that does reassembly chooses the
largest buffer available (18K) with which to work because it has no way to know the
size of the original IP packet until the last fragment is received. - 丢包问题.If one fragment of an IP datagram is dropped, then the entire original
IP datagram must be resent, and it will also be fragmented. - IP分片对防火墙的影响. a firewall might block the non-initial fragments because
they do not carry the information that would match the packet filter. This would
mean that the original IP datagram could not be reassembled by the receiving host.
If the firewall is configured to allow non-initial fragments with insufficient
information to properly match the filter, then a non-initial fragment attack through
the firewall could occur.
Avoid IP Fragmentation: What TCP MSS Does and How It Works
MSS
The TCP Maximum Segment Size (MSS) defines the maximum amount of data
that a host is willing to accept in a single TCP/IP datagram. This TCP/IP datagram
might be fragmented at the IP layer. The MSS value is sent as a TCP header
option only in TCP SYN segments. Each side of a TCP connection reports its MSS
value to the other side. Contrary to popular belief, the MSS value is not
negotiated between hosts. The sending host is required to limit the size
of data in a single TCP segment to a value less than or equal to the MSS
reported by the receiving host.
In order to assist in avoiding IP fragmentation at the endpoints of the TCP
connection, the selection of the MSS value was changed to the minimum buffer
size and the MTU of the outgoing interface (- 40). MSS numbers are 40 bytes
smaller than MTU numbers because MSS is just the TCP data size, which does not
include the 20 byte IP header and the 20 byte TCP header.
防止IP分片的方法
The way MSS now works is that each host will first compare its outgoing
interface MTU with its own buffer and choose the lowest value as the MSS to send.
The hosts will then compare the MSS size received against their own interface MTU
and again choose the lower of the two values.
实例
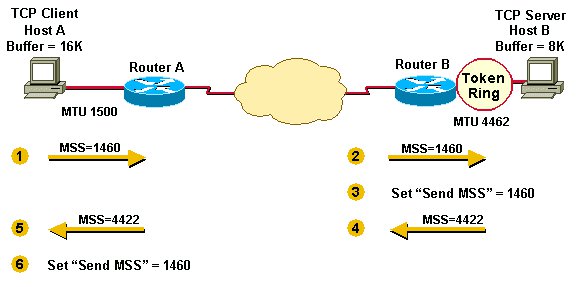
- Host A compares its MSS buffer (16K) and its MTU (1500 - 40 = 1460) and uses
the lower value as the MSS (1460) to send to Host B. - Host B receives Host A’s send MSS (1460) and compares it to the value of its
outbound interface MTU - 40 (4422). - Host B sets the lower value (1460) as the MSS for sending IP datagrams to Host A.
- Host B compares its MSS buffer (8K) and its MTU (4462-40 = 4422) and uses 4422 as
the MSS to send to Host A. - Host A receives Host B’s send MSS (4422) and compares it to the value of its
outbound interface MTU -40 (1460). - Host A sets the lower value (1460) as the MSS for sending IP datagrams to Host B.
1460 is the value chosen by both hosts as the send MSS for each other. Often
the send MSS value will be the same on each end of a TCP connection.Packets can
still become fragmented in the network between Router A and Router B if they encounter
a link with a lower MTU than that of either hosts’ outbound interface.
TODO TCP分段和IP分片之间的关系
The handling of TCP segments is more efficient than IP fragments. IP fragmentation is not quite as common as it was in earlier days of the Internet. Fragmentation is used when a network segment has a smaller MTU than the packet size. IP fragmentation is necessary if the MTU of the outgoing device is smaller than the packet size. See Chapter 9 for more details about IP fragmentation. TCP segmentation, however, is far more common because it is the underlying mechanism for the transport of streaming data that occurs in most network traffic.